| common denominator | A number that is a multiple of all of the denominators in a group of fractions. |
| composite number | A natural number that has at least one factor other than 1 and itself. |
| denominator | The bottom number of a fraction that tells how many equal parts are in the whole. |
| divisibility test | A rule that tells quickly whether dividing a number by another number can be done without leaving a remainder. |
| divisible | Can be divided by a number without leaving a remainder. For example, 20 is divisible by 4 because 20 ÷ 4 = 5 (no remainder). |
| divisor | The number that is being divided into the dividend in a division problem. In the problem 8 ÷ 2 = 4, 2 is the divisor. |
| equivalent fractions | Two or more fractions that name the same part of the whole. |
| even number | A whole number that is divisible by 2. |
| exponential notation | A notation that represents repeated multiplication using a base and an exponent. For example, 24 is notation that means 2 • 2 • 2 • 2. This notation tells you that 2 is used as a factor 4 times. 24 = 16. (Also called exponential form.) |
| factor | A number that is multiplied by another number or numbers to get a product. For example, in the equation 4 • 5 = 20, 4 and 5 are factors. |
| factor pair | A pair of numbers whose product is a given number. For example, 2 and 15 are a factor pair of 30 because 2 •15 = 30. Both 2 and 15 are factors of 30. |
| factor tree | A diagram showing how a number can be written as factors, and those factors written as a product of factors, and so on until only prime numbers are used. |
| fraction | An expression used to refer to a part of a whole. |
| improper fraction | A fraction in which the numerator is equal to or greater than the denominator. |
| least common denominator | (LCD) The least, or smallest, number that is a multiple of all the denominators in a group of fractions. |
| least common multiple | (LCM) The least, or smallest, number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. |
| like denominators | Denominators that are the same. |
| lowest terms | A fraction is in lowest terms if the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1. |
| mixed number | An expression in which a whole number is combined with a proper fraction. For example 5 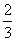 is a mixed number. |
| multiple | Any number that has a given number as a factor. For example, 4, 8, 16, and 200 are multiples of 4, because 4 is a factor of each of these numbers. |
| natural number | The numbers 1, 2, 3, 4 and so on. Also called counting numbers. |
| numerator | The top number of a fraction that tells how many parts of a whole are being represented. |
| prime factorization | A number written as the product of its prime factors. |
| prime number | A natural number with exactly two factors: 1 and the number itself. |
| product | The result when two numbers are multiplied. For example, the product of 4 • 5 is 20. |
| proper fraction | A fraction in which the numerator is less than the denominator. |
| reciprocal | A number that when multiplied by a given number gives a product of 1. For example, 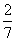 and and 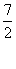 are reciprocals of each other. are reciprocals of each other. |
| simplest form | A fraction is in simplest form if the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1. |
| unlike denominators | Denominators that are different from each other. For example the fractions 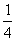 and and 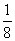 have different denominators, one denominator being 4 and the other denominator being 8. have different denominators, one denominator being 4 and the other denominator being 8. |
![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are reciprocals of each other.
are reciprocals of each other.![]() and
and ![]() have different denominators, one denominator being 4 and the other denominator being 8.
have different denominators, one denominator being 4 and the other denominator being 8.